Introduction to chemistry: Chapters
1, 2 and 3
- What
is chemistry? Study of
composition of matter.
- What
are the five major areas (and their definitions) of chemistry?
1) Organic chemistry:
Study of all matter containing carbon.
2) Inorganic chemistry:
Study of matter not containing carbon (usually non-living things).
3) Analytical Chemistry:
Study of the composition of substances.
4) Physical Chemistry:
Theories and experiments regarding the behavior of chemicals.
5) Biochemistry: Study
of chemistry in living organisms.
- Explain
the difference between pure and applied chemistry? In applied chemistry, scientists
apply knowledge to achieve certain goals (like developing new
technologies). In pure chemistry,
scientists gather knowledge for its own sake.
- What
is the composition of plastic? Plastics are also called polymers and
they are made up gigantic molecules.
- What
are the four major steps of the scientific method? Identify the problem; write a purpose,
experiment and conclude (if you want to go into more detail; the
experiment part includes collection of data; graphing/organizing of data
and the analysis of data).
- What
is an observation? Using your sensing to directly obtain information.
- What
are the different types of observations? Quantitative observations and
qualitative observations.
- What
is a quantitative observation? It examines properties of substances
that are numerical (the properties are numerical not the substances)
- What
is a qualitative observation? It examines properties of substances that
are not numerical (for example: color, odor, texture etc.)
MATTER AND CHANGE - Assembled by Mahima Kishore
1. What
is matter? Anything that takes up space and mass.
2. What
is mass? The amount of matter it contains (that’s a bad definition)…it’s
the amount of "stuffing" in an object.
3. What
is a substance? Only contain one kind of matter (sometimes known as pure
substances). All samples of the same substances have the same physical
properties.
4. What
is physical property? Quality or condition of a substance that can be
observed or measured without changing the substance’s composition. Ex: color,
solubility, odor, hardness, density, melting point, and boiling point.
5. What
is a solid? Matter with a tangible shape and volume. (Cannot be shrunken
into a smaller volume or shape…they only expand when slightly heated
"incompressible")
6.
**Physical state of a substance is also a physical form***
7. What
is a liquid? Type of matter that flows, has a fixed volume and takes the
shape of whichever container it is. They tend to expand (more than solids) when
heated so they are almost incompressible.
8. What
is a gas? It flows to take the shape and VOLUME of its container. Particles
are really quite apart.
9. What
is vapor? It is the gaseous form of a substance that is usually liquid.
10. What
is a physical change? Altering a material without changing its chemical
composition.
11. What
is a mixture? Physical blend of two or more pure substances. Their
compositions may vary
12. What is a homogeneous mixture? Homogeneous mixtures have the same composition in any given part of the sample. Homogeneous mixtures have definite composition and properties.
13. What is a heterogeneous mixture? ? It is a mixture that has no definite composition. Heterogeneous mixtures are not even all throughout. They are said to have phases which are parts of homogeneous compositions that can be mechanically separated from the overall heterogeneous mixture.
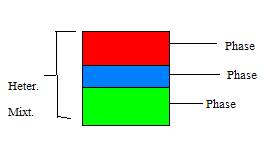
14. What’s
a phase? A part of a mixture that has uniform composition.
15. What
is distillation? Boil a liquid, then condense it…. by doing this you can
separate the components in a mixture (like distilled water)
16. What
are the two categories in which substances can be divided? Elements and
Compounds.
17. What
are elements? Simplest form of matter that exist under normal lab
conditions. They are building blocks for all other substances.
18. What
are compounds? Two or more elements chemically bonded together. They can be
separated into simpler matter only by chemical means. Properties of compounds
much different from those of the elements that compose it.
19. What
are the two groups in which pure substances can be classified? Elements and
Compounds.
20. What
are elements? They are simplest form of matter that can exist under lab
conditions. They cannot be separated into simpler forms by chemical means. They
are building blocks for all other substances.
21. What
are compounds? Two or more elements chemically bond to form compounds.
These are substances that can only be separated by chemical means.
22. Properties
of compounds are very different from their components; true or false? True.
23. What
is a chemical symbol? One or two letters that represent each element.
24. What
is a chemical reaction? When one or more substances form to make a new
substance.
25. What
are reactants? The starting substances in a reaction
26. What
is a product? The result of a chemical reaction.
27. What
is a chemical property? The ability of a substance to undergo chemical
change and to produce new substances. Chemical properties are only observed
when a substance undergoes chemical change.
28. What
are the indicators that a chemical reaction has taken place? They are:
change in color, heat, generation of a gas and the change on the surface of a
solid.
29. What
is the law of Conservation of Mass? It says that during physical or
chemical changes, mass is not created or destroyed; it is conserved.
30. What is a solution? It is a type of homogeneous mixture. It consists of one or more substances, which are the solutes, dissolved in another substance called the solvent. Solvents are usually water but they don’t have to be. A common polar solvent is water.
Scientific Measurement : Assembled by Mahima
Kishore
1. What
are qualitative measurements? They give results in a descriptive
non-numerical form.
2. What
are quantitative measurements? They give results in a numerical forms.
3. What
is scientific notation? Short for a writing a number that is incredibly
small or very large. It is written as a coefficient times ten raised to a
power. For example 3500 would be 3.5 X 103
4. Define
Accuracy? How close the measurement is the actual or accepted value.
5. Define
precision? How close the measurements are to each other.
6. What
is accepted value? It is the correct value, derived from reliable
resources.
7. What
is experimental value? Value measured in the lab.
8. What
is the percent error? The absolute value of the quantity accepted value
minus experimental value, over the accepted value, all which multiplied by 100.
( |Value accepted – Value measured | )
----------------------------------------------- X 100 = percentage error
Value accepted
9. What
are significant figures? The significant figures in a measurement include
all the places that are known and the last place, which is estimated (also
known as the uncertainty).
10. What
are the rules of determining whether a number is significant? 1. All
non-zero numbers are significant. 2. Zeros appearing between non-zero digits
are significant. Left most zeros before non zero digits are not significant. 3.
Zeros at the end of a number and to after a decimal point are always
significant.
11. What are the rules for rounding in addition/subtraction? Adding and subtracting with precision: When doing calculations involving measurements, the answer can only be as accurate as the LEAST accurate measurement made. The answer must be rounded off to the same column as the LEAST precise measurement used in the calculation. For Example: 246.58 – 87.3 = calculated answer: 159.28, rounded to the correct precision: 159.
12. What
is the formula for density? Density equals the mass over volume.
13. What
is specific gravity? Ratio/comparison of the density of a substance to the
density of a reference substance (usually water) of the same temperature.
14. What
is the temperature of an object? The temperature of an object determines
the direction of heat transfer.
15. ***Make
sure you know the basic metric untis: meters (for length), kilometers (for
weight), liters (for volume) and their divisions.
16. Multiplying
and dividing in significant figures: The answer must be rounded off to the
same number of significant figures as the least accurate measurement used in
the calculation (the number with the least number of significant figures). For
example: multiply 34.0 and .0921084.
The first number as 3 sig figs and the second one has 6. Calculator
answer: 3.1316856 . Rounded to correct
accuracy (three significant figures) 3.13
17. Significant
figures with scientific notation: Count significant figures only for the
first part of the notation.
18. What are some important rules of scientific notation: a) Scientific notations is a rational number times ten raised to a power. b) That rational number must be greater than zero and less than 10. c) The power of ten indicates how many places the decimal point has been moved. d) If the original number is large (greater than one) then the exponent is positive and the original number is small (less than one) then the exponent is negative.
19. How do you multiply in scientific notation? Multiply the first part as usual and ADD the exponents. SAMPLE PROBLEM: (2 X 104) times (3X 105): Multiply three and two as usual and add the powers of ten: 6 X 109
20. How do you divide in scientific
notation? Divide the first part as usual and SUBTRACT the exponents. SAMPLE PROBLEM: (6 X 109) divided by (3 X 10 5).
Divide six by three as usual and subtract the powers of then. 2 X 104
21. Some examples of scientific
notations:
|
Regular Form |
Scientific Notation |
|
3,500,000 |
3.5 X 106 |
|
400 |
4 X 102 |
|
.000062 |
6.2 X 10-5 |
|
.007419 |
7.419 X 10-3 |